How tuberculosis destabilises the mental moorings of patients
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus context: GS IV Science and Technology
Tuberculosis and Mental Health: An Integrated Perspective for UPSC Preparation
Tuberculosis (TB), a long-standing public health challenge in India, is not just a medical issue but a multidimensional crisis affecting mental health, social equity, and economic well-being. In 2022, India reported 2.42 million TB cases, making it a focal area for public health interventions. Understanding the interplay between TB and mental health is crucial for aspiring policymakers preparing for the UPSC examination, especially under topics like health, governance, and social issues.
Understanding the Mental Health Impact of TB
TB is often accompanied by a significant mental health burden due to:
- Stigma and Ostracism: Fear of contagion, associations with poverty, and perceptions of unhealthy behavior lead to societal and self-stigma. This impacts the mental well-being of patients from diagnosis to treatment.
- Treatment Challenges: The prolonged and often painful TB treatment, marked by extreme side effects like physical scarring and psychotic episodes, further exacerbates mental health conditions. Studies indicate that up to 84% of TB patients experience depression.
The Bidirectional Link Between TB and Mental Health
The TB-mental health nexus is a two-way association:
- TB Impact on Mental Health: Stigma, prolonged treatment, and side effects lead to hopelessness, impaired decision-making, and treatment non-adherence.
- Mental Health’s Role in TB Vulnerability: Depression and stress weaken the immune system, increasing TB susceptibility. Addiction to substances like alcohol and tobacco, often linked to mental health disorders, further elevates the risk.
Policy and Programmatic Gaps
Despite TB’s significant burden, India’s national TB programmes (NTPs) lack adequate focus on mental health:
- Only two of 26 surveyed countries’ NTPs screen for mental disorders.
- Routine mental health screening and psychological support are absent from standard TB care protocols.
Way Forward: A Holistic Approach
To address TB effectively, a comprehensive strategy integrating mental health into TB care is essential:
- Mental Health Screening and Support:
- Incorporate routine mental health screenings (e.g., simple, self-administered questionnaires).
- Provide psychological support during treatment to alleviate stress and improve outcomes.
- Leveraging Technology:
- Use smartphone-based cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) apps for mild depression.
- Expand AI-driven solutions for remote mental health support.
- Community Engagement:
- Build support groups to destigmatize TB and mental health.
- Empower communities to co-design policies and programmes.
- Strengthening Mental Health Services:
- Train more psychiatrists to bridge the treatment gap.
- Ensure pathways for timely referrals and interventions for severe cases.
Significance for India’s TB Elimination Goals
Mental health support is not just a compassionate approach but a critical strategy to arrest TB transmission. Addressing mental health improves treatment adherence, reduces dropout rates, and enhances outcomes. Recognizing TB and mental health as interconnected epidemics underscores the need for integrated policy measures to achieve India’s goal of TB elimination by 2025.
Is Syria’s Assad regime in danger?
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus context: GS III Internal Security
Syria’s Assad Regime: Challenges Amidst Renewed Civil War
The Syrian civil war, which began in 2011 amidst Arab Spring-inspired anti-government protests, had seemingly entered a frozen phase by 2016. However, recent developments indicate a resurgence of conflict as Islamist militants have made dramatic territorial gains, threatening the regime of President Bashar al-Assad. This evolving crisis offers critical insights into geopolitics, regional stability, and international intervention, making it a significant topic for UPSC aspirants preparing for
Historical Context and the Role of Russia (2016)
In 2015, the Assad regime was on the brink of collapse, controlling only Damascus and the Alawite-dominated coastal cities. Multiple factions, including the Free Syrian Army, al-Qaeda-affiliated Jabhat al-Nusra, and the Islamic State (IS), controlled significant parts of Syria.
- Russia’s Role: Russian President Vladimir Putin’s military intervention in 2015 proved decisive for the Assad regime. Russian air power, combined with support from Iran and Hezbollah, enabled Syrian forces to launch counteroffensives.
- Recapture of Aleppo (2016): By December 2016, Aleppo, Syria’s second-largest city, was retaken after intense battles. This marked a turning point in the civil war, consolidating regime control over key territories and reducing the influence of rebel factions.
Current Actors and the Resurgence of Conflict
Syria today is a complex battleground involving three main actors:
- The Assad Regime: Backed by Russia, Iran, and Shia militias, the regime remains the most significant force. However, its resources have been stretched thin due to geopolitical shifts.
- Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF): Predominantly Kurdish militias, including the People’s Protection Forces (YPG), control northeastern Syria. The regime and the Kurds have maintained a delicate truce, avoiding direct confrontations.
- Hayat Tahrir al-Sham (HTS): The dominant anti-regime force in Idlib, HTS evolved from the al-Qaeda-affiliated Jabhat al-Nusra. Led by Abu Mohammad al-Julani, HTS has built a parallel state in Idlib and recently launched a surprise offensive.
Understanding Hayat Tahrir al-Sham (HTS)
- Origins: HTS traces its roots to Jabhat al-Nusra, an al-Qaeda branch in Syria, established under Julani’s leadership. Over time, HTS rebranded itself to distance from al-Qaeda while retaining its Islamist ideology.
- Tactical Advances: HTS, along with the Turkey-backed Syrian National Army (SNA), leveraged the regime’s vulnerabilities to achieve swift territorial gains, including the capture of Aleppo.
Geopolitical Shifts and the Militant Offensive
Several factors enabled the militants to capitalize on the regime’s weaknesses:
- Russian Withdrawal: Russia’s focus shifted to its war in Ukraine, reducing its military presence in Syria.
- Iranian Challenges: Key Iranian figures, such as Qassem Soleimani, instrumental in supporting Assad, have been lost to targeted strikes, weakening Iran’s operational capacity.
- Hezbollah’s Repositioning: The group’s focus on conflicts with Israel has limited its ability to assist in Syria.
- Turkish Backing: Turkey reportedly supported HTS and the SNA, facilitating their advances and complicating the regional dynamics.
Implications of the Recent Conflict
- Territorial Shifts: Within a week, militants have doubled their territorial control, capturing Aleppo, parts of Hama, and northeastern regions from Kurdish rebels.
- Regime Vulnerability: The swift collapse of regime forces in northern Syria has emboldened smaller rebel factions across the country, leading to renewed clashes in the south.
- Humanitarian Crisis: The renewed fighting threatens to exacerbate Syria’s already dire humanitarian situation, with millions of civilians at risk.
What Lies Ahead for the Assad Regime?
The Assad regime faces a precarious future:
- Military Reinforcements: Iran has mobilized Iraqi militias, such as Kataib Hezbollah, to bolster regime forces. However, these efforts may not be sufficient to reverse militant advances.
- Strategic Challenges: The regime’s inability to arrest territorial losses raises questions about its long-term stability.
- Potential for Prolonged Conflict: With militants sensing an opportunity to expand control, Syria appears poised for another extended period of bloodshed.
Conclusion
The Syrian civil war underscores the complexity of modern conflicts, where local grievances intertwine with global power dynamics. Understanding the evolving situation and its broader implications equips future policymakers to address similar challenges in a nuanced manner.
Domestic industry stares at months long copper shortage as quality norms kick in
Source: Indian express
Syllabus context: GS III issues relating to Planning, Mobilization of Resources, Growth, Development
Copper Industry in India: Challenges and Opportunities
Why in News?
The Quality Control Order (QCO) on refined copper, effective December 1, 2023, has halted imports from Japanese suppliers—India’s primary source of refined copper—pending Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) certification. This delay threatens a potential supply crunch for over three months, impacting the downstream industry.

Significance of Copper
- Physical Properties: High conductivity, malleability, corrosion resistance.
- Recyclability: 100% recyclable without quality loss, making it eco-friendly.
- Applications:
- Electrical Industry: Wiring, motors, transformers.
- Construction: Roofing, plumbing, heating systems.
- Automobiles: Wiring, radiators, connectors.
- Electronics: Integrated circuits, semiconductors.
- Renewable Energy: Wind turbines, solar panels, EVs.
Copper Mining and Reserves in India
- Mining Processes: Open-pit and underground mining, leaching, refining (smelting, electrolytic methods).
- Major Reserves:
- Rajasthan: Khetri and Jhunjhunu belt.
- Madhya Pradesh: Malanjkhand (largest open-pit mine).
- Jharkhand: Singhbhum copper belt.
- Production Facilities: Operated primarily by Hindustan Copper Limited (HCL).
Global Copper Exporters
- Chile: Dominates with over 30% of global production.
- Peru, China, U.S., and Australia: Other key exporters.
Challenges in India’s Copper Industry
- Resource Constraints: Limited reserves and dependence on imports (30-40%).
- High Costs: Rising energy and labor costs hinder competitiveness.
- Environmental Concerns: Deforestation and pollution from mining operations.
- Policy Issues: Regulatory delays and inconsistent policies.
- Sterlite Plant Closure: The 2018 shutdown of Vedanta’s Sterlite plant in Tamil Nadu reduced domestic self-sufficiency, increasing import reliance.
Government Initiatives
- National Mineral Policy (NMP) 2019: Aims to enhance domestic mining and reduce imports.
- Mining Reforms: Streamlined auction and resource allocation processes.
- Renewable Energy Push: Boosts demand for copper in EVs and solar projects.
- Make in India: Encourages investments to strengthen domestic manufacturing.
Impact of the QCO on Refined Copper
- Import Dependence: Japan accounts for 80% of India’s refined copper imports, valued at ₹16,500 crore in 2023-24.
- BIS Certification:
- Certification involves non-standard resistivity tests, requiring BIS-approved Indian labs.
- Delays have disrupted shipments since October 2023.
- Supply Disruption: A 90-day gap in copper supply is anticipated, impacting electrical, wire, and cable manufacturing industries.
Economic and Industrial Implications
- Production Delays: Input shortages threaten project timelines and increase costs.
- SME Vulnerability: Medium and small enterprises bear the brunt of disruptions.
- Stakeholder Concerns:
- Requests for a four-month extension for QCO implementation.
- Pending BIS certifications since January 2023 delay imports.
Future Outlook
- Domestic Expansion:
- Adani’s Kutch refinery aims to ramp up production by 2025, easing supply constraints.
- Policy Adjustments:
- Export-oriented units exempted from QCO requirements.
- Calls for expedited BIS certification and temporary relaxation of QCO norms.
Additional Insights
- Difference Between Mining and Quarrying:
- Mining: Extracting buried materials below the earth’s surface.
- Quarrying: Extracting materials directly from the surface.
- Iron Ore to Steel Conversion:
- Involves direct reduction of iron ore using hydrogen, enabling steel production without fossil fuels.
Conclusion: India’s copper industry faces short-term challenges due to policy adjustments, but long-term prospects appear favorable with domestic capacity expansion and supportive policies. The focus on renewable energy and infrastructure growth further emphasizes the critical role of copper in India’s economic development.
Bhutan and India discuss Gelephu, hydel power plans
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus Context: GS II India and neighbourhood relations
Gelephu Mindfulness City Project and Punatsangchhu-II Hydropower Project: Strengthening India-Bhutan Cooperation
Gelephu Mindfulness City Project
- Location: Gelephu, a strategic southern town in Bhutan near the Indian border.
- Objective: Aimed at creating a sustainable urban development model to enhance prosperity, well-being, and economic integration between Bhutan and neighboring Indian regions.
- Key Features:
- Focus on sustainability, mindfulness, and regional development.
- Plans to boost cross-border connectivity and economic linkages.
- Aligns with Bhutan’s vision for Gross National Happiness (GNH) and India’s emphasis on regional prosperity.
- India’s Role:
- Committed to financial and technical assistance, reflecting its commitment to regional cooperation and mutual growth.
- Project reinforces India-Bhutan relations by supporting Bhutan’s development goals and enhancing bilateral connectivity.
Punatsangchhu-II Hydropower Project
- Location: Punakha District, Bhutan.
- Geographical Importance:
- Situated on the Punatsangchhu River, formed by the confluence of Phochhu and Mochhu rivers originating in the Himalayas.
- The river is a tributary of the Brahmaputra, emphasizing its transboundary significance for water resources.
- Significance for Bhutan:
- A key component of Bhutan’s hydropower-driven economy, contributing to revenue and energy security.
- Strengthens Bhutan’s export capacity, primarily to India, supporting its economic growth.
- India’s Role:
- Active funding, technical expertise, and infrastructure collaboration ensure the project’s progress.
- Reflects India’s commitment to bilateral energy cooperation, enhancing clean energy production and fostering mutual interdependence.
Strategic and Regional Implications
- Strengthened India-Bhutan Ties:
- Projects symbolize India’s Act East policy and its role as a trusted development partner.
- Foster mutual economic benefits, regional stability, and environmental sustainability.
- Regional Connectivity and Energy Security:
- Hydropower projects like Punatsangchhu-II play a pivotal role in advancing energy trade and sustainable development in South Asia.
- The Gelephu Mindfulness City Project enhances cross-border infrastructure and people-to-people connectivity.
- Alignment with Global Goals:
- Supports the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by promoting clean energy, sustainable urbanization, and regional cooperation.
Key Highlights of the recent India-Bhutan Bilateral Talks:
- Petroleum Agreement: Both nations signed an agreement ensuring a reliable supply of petroleum products from India to Bhutan
- Food Safety Collaboration: Bhutan’s Food and Drug Authority and India’s FSSAI signed an agreement to enhance cooperation in food safety measures, facilitating trade and reducing compliance costs.
- Energy Efficiency and Conservation: An MoU on energy efficiency and conservation reflects a commitment to sustainable development, with India assisting Bhutan in enhancing energy efficiency and promoting the use of energy-efficient appliances.
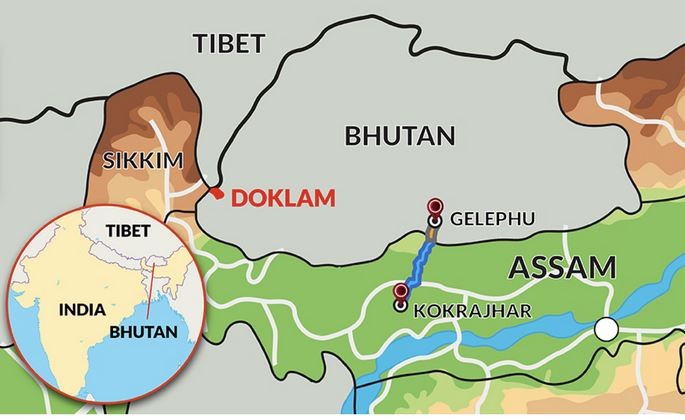
- Border Dispute Resolution: Ongoing discussions between China and Bhutan to resolve their border dispute were discussed, particularly in the Doklam region, with implications for regional security.
- Bhutan’s Regional Economic Hub in Gelephu: Plans for a regional economic hub in Gelephu aim to foster regional development and connecti
Issues between the two countries:
- Border Dispute: Disputes over the exact demarcation of the border between the two countries.
- Hydropower Projects: Concerns in Bhutan over environmental and social impacts from the project. Also, Bhutan has sought greater revenue from these projects
- Trade Imbalance:Bhutan is heavily dependent on India for its imports.
- Cross-Border Movement: Bhutan has restricted the cross-border movement of Indian workers, citing concerns over the impact on Bhutan’s culture and society.
- Political Interference:Bhutan has accused India of interfering in its internal affairs, particularly during the 2013 elections.
Conclusion
India’s partnership with Bhutan through transformative initiatives like the Gelephu Mindfulness City Project and Punatsangchhu-II Hydropower Project highlights the importance of bilateral collaboration in achieving shared goals of development, prosperity, and sustainability. These projects strengthen regional connectivity, enhance energy security, and reaffirm India’s leadership role in promoting sustainable growth in South Asia.