Finding a home away from home after 2004 tsunami
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus: GS III Disaster management
Finding a Home Away From Home: Lessons from the 2004 Tsunami for India’s Disaster Resilience and Management Framework
Introduction
The Indian Ocean tsunami of December 26, 2004, triggered by a 9.1-magnitude earthquake near Sumatra, remains one of the deadliest natural disasters in history. Spanning 14 countries and claiming over two lakh lives, its catastrophic impact was especially severe along India’s eastern coastline. Tamil Nadu’s Nagapattinam district bore the brunt, with over 6,000 fatalities and widespread displacement.
Two decades on, Nagapattinam’s recovery journey underscores critical lessons for India’s disaster management and resilience framework. From child welfare successes to persistent housing challenges, the disaster exposed gaps in governance, long-term planning, and community engagement.
Child Welfare: A Model for Rehabilitation Success
The Annai Sathya Government Children’s Home in Tamil Nadu stands out as a beacon of hope and resilience in post-disaster recovery. Established in 2005 to shelter 128 orphaned children and protect them from exploitation, the home exemplifies the importance of targeted, child-centric social interventions.
Today, the success stories of its alumni, such as Meena, a nursing graduate, and Tamilarasi, now a vocational trainer, illustrate the transformative potential of sustained emotional and educational support. Annual reunions foster a sense of belonging and emotional healing, showcasing the importance of integrating long-term psychosocial care into disaster management frameworks.
Key Takeaway: Children, among the most vulnerable populations during disasters, require not just immediate protection but sustained support. Child-centric policies must become an integral part of India’s disaster management strategy.
Housing Challenges: Lessons from Fisherfolk Communities
For the fisherfolk of Nagapattinam’s twin villages of Akkarapettai and Keechankuppam, the path to recovery has been fraught with systemic challenges. While NGOs undertook housing rehabilitation projects, they often overlooked the occupational and cultural needs of the community.
- Resettled in apartment-style housing, fisherfolk found these spaces ill-suited for storing fishing equipment or processing daily catches.
- Substandard construction left many homes vulnerable, forcing families to live under unsafe conditions.

Community Voices:
- R.M.P. Rajendra Nattar, President of the Indian National Fishermen Union, lamented, “We have become refugees in our own country.”
- Rajalakshmi, a resident, noted, “Our homes are unsafe. The roof could collapse anytime.”
Key Takeaway: Community participation is critical in designing culturally appropriate and sustainable rehabilitation efforts. Collaborative planning ensures that infrastructure addresses the unique needs of affected populations.
Strengthening Disaster Management: Insights from Nagapattinam
The tsunami of 2004 exposed glaring deficiencies in India’s disaster management mechanisms. While immediate relief efforts were commendable, long-term rehabilitation revealed systemic challenges.
1. Prioritizing Community-Centric Recovery
Disaster management must place affected communities at the core of decision-making. The neglect of fisherfolk’s needs in housing projects underscores the need for inclusive, participatory approaches.
2. Institutional Accountability and Transparency
Failures in housing rehabilitation highlight the importance of robust monitoring mechanisms. Independent audits and transparent governance are essential to prevent financial mismanagement and ensure quality outcomes.
3. Emphasizing Psychosocial Support
Post-disaster trauma requires long-term psychological support, particularly for vulnerable groups like children and women. Institutions like the Annai Sathya Children’s Home demonstrate the value of integrating emotional rehabilitation into recovery frameworks.
4. Investing in Resilient Infrastructure
Substandard construction in post-tsunami housing underscores the need for disaster-resilient infrastructure. Strict adherence to building codes and the use of sustainable materials are crucial.
5. Building Local Capacity
Empowering communities through training, disaster preparedness drills, and awareness campaigns can significantly enhance their ability to respond effectively.
6. Strengthening Governance and Coordination
Effective disaster management requires seamless coordination between central, state, and local authorities. Unified command structures and clear roles for stakeholders are essential for efficient response and recovery.
7. Leveraging Technology
Advancements in early warning systems, GIS, and real-time communication have revolutionized disaster management. Expanding access to these tools in vulnerable areas is imperative.
Policy Recommendations
- Promote Community-Driven Recovery: Engage local communities in vulnerability assessments and planning to ensure solutions are practical and inclusive.
- Enhance NDMA and SDMA Capacities: Strengthen the institutional framework with increased funding, staffing, and technology.
- Integrate Climate Adaptation: Incorporate climate-resilient strategies to address the growing frequency of disasters.
- Foster Regional Collaboration: Partner with organizations like SAARC, BIMSTEC, and BRICS to enhance cross-border disaster response.
- Ensure Equity and Inclusivity: Address intersectional vulnerabilities, ensuring support for marginalized groups such as women, LGBTQIA communities, and the disabled.
Conclusion
The 2004 tsunami not only tested India’s resilience but also exposed critical gaps in its disaster management systems. As climate change increases disaster risks, the lessons from Nagapattinam offer invaluable insights into building a more robust, inclusive, and sustainable framework.
By prioritizing community engagement, transparent governance, and resilient infrastructure, India can transform its disaster management landscape, ensuring a safer and more equitable future for all.
₹45,000-cr. Ken-Betwa link project launched
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus: GS II Governance
Ken-Betwa River Linking Project: A Landmark Initiative in Interlinking of Rivers
Prime Minister Narendra Modi laid the foundation stone for the Ken-Betwa River Linking Project (KBLP) in Khajuraho, Madhya Pradesh, marking a significant step towards addressing water scarcity in India’s drought-prone regions, particularly Bundelkhand. This ambitious initiative, the first under the National Perspective Plan for river interlinking, aims to transfer surplus water from the Ken River to the Betwa River, fostering agricultural growth, water security, and regional development.
About the Ken-Betwa Link Project (KBLP)
The Ken-Betwa Link Project involves diverting water from the Ken River to the Betwa River, both tributaries of the Yamuna.
Key Features:
- Infrastructure: Includes a 73.8-meter-high Daudhan Dam on the Ken River in Madhya Pradesh’s Chhattarpur district, a 221-km canal, and a 2-km tunnel.
- Project Phases:
- Phase I: Construction of the Daudhan Dam, Ken-Betwa Link Canal, and associated tunnels and powerhouses.
- Phase II: Development of the Lower Orr Dam, Bina Complex Project, and Kotha Barrage.
- Timeline: The Ministry of Jal Shakti has proposed an implementation period of eight years for the project.
Historical Background
The project was conceptualized in the 1980s to address water scarcity in Bundelkhand but faced delays due to unresolved inter-state water-sharing disputes. After years of negotiations, a breakthrough was achieved on March 22, 2021, when a memorandum of agreement was signed among the Ministry of Jal Shakti and the governments of Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh.
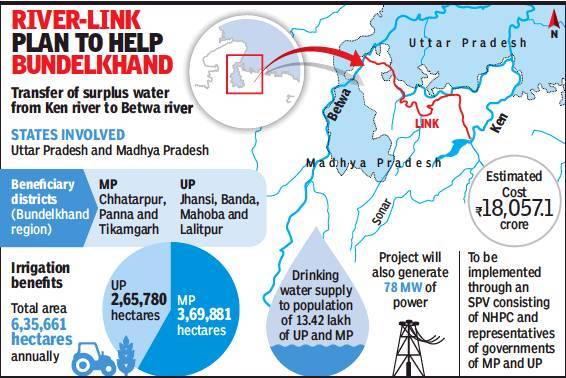
Regions and Communities Benefiting
The project is designed to transform the Bundelkhand region, spanning 13 districts in Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh.
- Madhya Pradesh: Key districts include Panna, Tikamgarh, Chhatarpur, Sagar, Damoh, Datia, Vidisha, Shivpuri, and Raisen.
- Uttar Pradesh: Beneficiary districts include Banda, Mahoba, Jhansi, and Lalitpur.
Anticipated Benefits:
- Irrigation: Annual irrigation for 10.62 lakh hectares, benefitting 8.11 lakh ha in Madhya Pradesh and 2.51 lakh ha in Uttar Pradesh.
- Drinking Water: Provision for 62 lakh people.
- Power Generation: Production of 103 MW hydropower and 27 MW solar power.
Environmental and Social Concerns
Environmental Impacts
- Deforestation:
- Around 98 sq km of Panna National Park will be submerged, resulting in the loss of 2–3 million trees.
- Threat to Wildlife:
- Tigers: The dam’s location within the Panna Tiger Reserve may jeopardize the successful tiger reintroduction program, which revived the tiger population after local extinction in 2009.
- Gharials and Vultures: Adverse impacts on the Ken Gharial Sanctuary and vulture nesting sites downstream.
- Hydrological Concerns:
- Research by IIT-Bombay indicates potential disruptions in land-atmosphere feedback, reducing September rainfall by up to 12%.
- Experts have called for greater transparency in hydrological data to assess the project’s impact comprehensively.
Social Impacts
- Displacement:
- The project will displace 5,228 families in Chhatarpur and 1,400 families in Panna district due to land acquisition and submergence.
- Inadequate Compensation:
- Affected communities, particularly in Panna district, have protested against inadequate compensation and limited benefits, exacerbating social tensions.
Controversies and Criticism
- Wildlife and Environmental Clearances:
- The Supreme Court’s Central Empowered Committee (CEC) questioned the wildlife clearance and the project’s economic feasibility.
- Violation of Precedents:
- The Union Environment Ministry’s approval for construction within the Panna Tiger Reserve’s core area violates norms prohibiting large-scale infrastructure projects in tiger reserves.
Significance in the Context of India’s Water Management
The KBLP is a flagship project under India’s National Perspective Plan (1980) for interlinking rivers, aimed at resolving water disparities between water-surplus and water-deficit regions.
Strategic Importance:
- Boosting Agricultural Productivity:
- By addressing water scarcity in Bundelkhand, the project aims to improve agricultural yield and foster economic development in this drought-prone region.
- Setting a Precedent for Future River-Linking Projects:
- Successful implementation could pave the way for other interlinking projects, reinforcing India’s water security.
Way Forward
Mitigating Environmental Concerns:
- Implement compensatory afforestation programs and habitat restoration initiatives for wildlife conservation, particularly for tigers and gharials.
- Establish a robust environmental monitoring mechanism to mitigate potential hydrological and ecological disruptions.
Addressing Social Issues:
- Ensure fair and transparent compensation mechanisms for displaced families, coupled with livelihood rehabilitation programs.
- Strengthen public participation and stakeholder engagement to address concerns of local communities effectively.
Enhancing Project Governance:
- Conduct periodic reviews of project execution to ensure adherence to environmental, social, and technical standards.
- Promote inter-state cooperation to resolve disputes swiftly and efficiently.
Conclusion
The Ken-Betwa Link Project represents a significant step toward sustainable water management and regional development in India. While it promises transformative benefits for the Bundelkhand region, its success hinges on balancing developmental needs with environmental sustainability and social justice. As the first interlinking project under the National Perspective Plan, it has the potential to set a benchmark for future initiatives, provided its challenges are addressed comprehensively and inclusively.
US FDA approves use of weight loss drug for sleep apnoea: Here’s all you need to know
Source: The Indian Express
Syllabus: GS III Science and Technology
FDA Approval of Tirzepatide (Zepbound) for Obstructive Sleep Apnoea (OSA): A Landmark Development in Sleep Disorder Management
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Tirzepatide, marketed as Zepbound, as the first drug-based treatment for Obstructive Sleep Apnoea (OSA). This approval marks a significant milestone, introducing a pharmaceutical option for individuals with moderate to severe OSA, particularly those who are obese or overweight. The drug is recommended alongside a low-calorie diet and increased physical activity to maximize its efficacy.
This development underscores Tirzepatide’s diverse therapeutic potential, extending beyond its established use in managing type-2 diabetes and obesity. By addressing fat accumulation around the neck—a key contributor to throat muscle laxity—Zepbound represents a novel approach to managing OSA.
Understanding Obstructive Sleep Apnoea (OSA)
Types of Sleep Apnoea:
- Obstructive Sleep Apnoea (OSA):
- The most prevalent form, caused by physical obstruction of the airway.
- Central Sleep Apnoea:
- Arises when the brain fails to send appropriate signals to breathing muscles.
- Complex Sleep Apnoea Syndrome:
- A combination of OSA and central sleep apnoea.
About OSA:
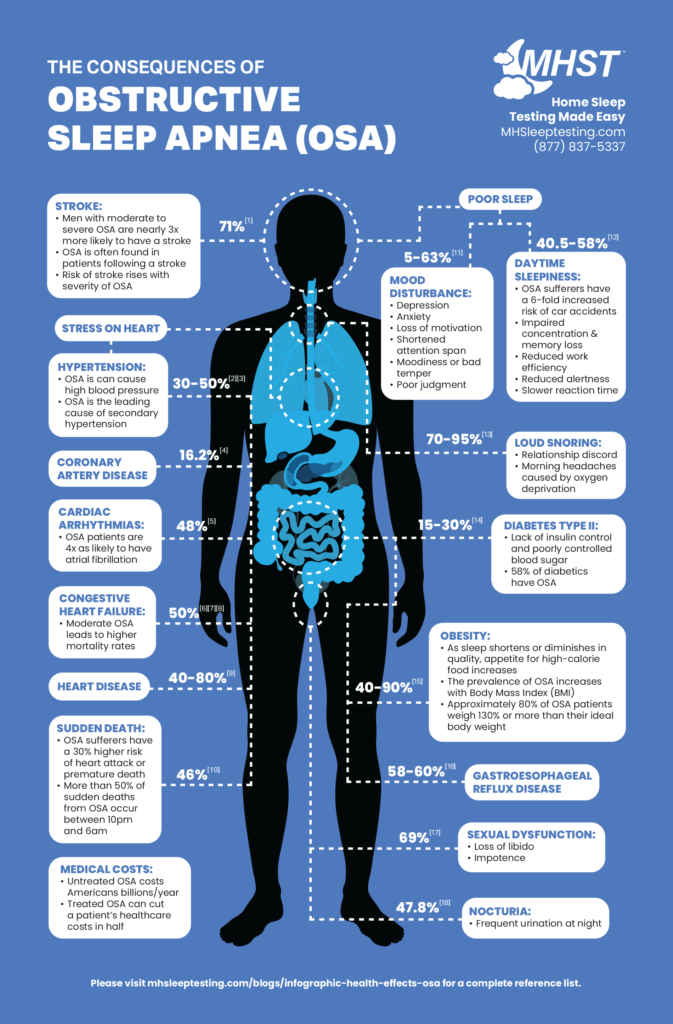
OSA is a sleep disorder characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing due to relaxation of throat muscles, resulting in brief awakenings and disrupted sleep quality. Individuals with OSA often experience excessive daytime fatigue, loud snoring, and frequent nocturnal awakenings, despite a full night’s sleep.
Link Between Obesity and OSA
Key Contributors:
- Abdominal Fat: Reduces lung capacity, increasing the risk of airway obstruction.
- Neck Fat and Tongue Floppiness: Excess fat deposits around the neck and tongue can block airways during sleep.
Prevalence:
- Over 50% of OSA patients are obese, and 25% are overweight.
- Obesity is identified as a significant risk factor, with smaller lungs and other anatomical changes exacerbating the condition.
Other Risk Factors:
- Aging, smoking, and genetic predisposition also contribute to OSA.
Current Treatment Landscape for OSA
Traditional Approaches:
- Positive Airway Pressure Machines (CPAP):
- Devices that deliver pressurized air to keep airways open during sleep.
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Weight loss, exercise, and dietary modifications.
- Medications:
- Prescribed to enhance sleep quality and manage associated symptoms.
Gap in Treatment Options:
- Until the approval of Zepbound, there was no drug specifically targeting the root cause of OSA.
Zepbound: A Novel Approach to Treating OSA
Mechanism of Action:
Zepbound activates intestinal hormone receptors, including:
- Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1).
- Glucose-dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide (GIP).
These actions result in reduced appetite and lower food intake, facilitating weight loss, which indirectly mitigates OSA symptoms.
Manufactured by:
- Eli Lilly and Co., Zepbound is approved for individuals with obesity or overweight conditions coupled with related health issues, such as:
- Type-2 diabetes.
- High cholesterol.
- Hypertension.
Potential Benefits of Zepbound
- Weight Reduction:
- By addressing obesity, Zepbound alleviates key contributors to OSA, such as neck fat and tongue laxity.
- Multifaceted Health Improvements:
- Studies suggest Zepbound could benefit additional conditions associated with obesity, including cardiovascular diseases, type-2 diabetes, and high blood pressure.
- Enhanced Patient Compliance:
- The introduction of a drug-based therapy for OSA provides an alternative for individuals unable to adapt to CPAP devices or those who face challenges in achieving significant weight loss through lifestyle changes alone.
Challenges and Future Research
- Understanding Mechanisms: Additional studies are underway to explore Zepbound’s mechanisms beyond weight loss and its impact on related disorders.
- Long-term Efficacy: Assessing the sustained benefits of Zepbound in managing OSA and associated complications.
- Accessibility: Ensuring affordability and availability for a broader patient base.
Conclusion
The FDA’s approval of Tirzepatide (Zepbound) as the first pharmaceutical intervention for OSA marks a paradigm shift in the treatment of sleep disorders. By addressing the underlying role of obesity in OSA, Zepbound offers a comprehensive solution to a condition that has long relied on mechanical devices and lifestyle interventions. This development also reinforces the importance of interdisciplinary approaches in addressing complex health issues, paving the way for further innovations in sleep medicine and obesity management.
What is Australia’s Online Safety Amendment about?
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus: GS II Polity and Governance
Australia’s Online Safety Amendment: A Step Toward Protecting Children Online
Introduction
Australia’s House of Representatives recently passed the Online Safety Amendment (Social Media Minimum Age) Bill, 2024, which introduces strict measures to prevent children under 16 from creating accounts on social media platforms. This legislation aims to mitigate online harms faced by minors while balancing privacy concerns and stakeholder responsibilities.
Key Provisions of the Law
- Objective:
- The amendment seeks to reduce the risk of harm to age-restricted users (defined as Australian children below 16 years) from exposure to online platforms.
- Applicability:
- Age-Restricted Social Media Platforms (ARSMPs): Platforms facilitating online social interactions and allowing content sharing will be subject to this law.
- Platforms like TikTok, Facebook, Snapchat, Instagram, Reddit, and X are included, while certain services may be excluded.
- Implementation Framework:
- ARSMPs must take reasonable steps to prevent children under 16 from creating accounts.
- Failure to comply may attract a maximum civil penalty of AUD 49.5 million.
- Guidelines defining “reasonable steps” will be formulated by the eSafety Commissioner.
- Age Verification:
- All account holders on ARSMPs must verify their age, guided by ongoing trials to identify acceptable age-assurance technologies.
- Timeline:
- The law will take effect no earlier than 12 months post-enactment to allow for consultations with stakeholders.
Privacy Concerns and Safeguards
- Data Privacy Risks:
- Age-verification technologies may collect sensitive personal data, posing privacy challenges.
- The proposed law mandates that entities collecting personal information for age verification must destroy the data once its purpose is served.
- Unauthorized use or disclosure of such information will invite penalties under the Privacy Act, 1988.
- Digital Duty of Care:
- The government plans to introduce additional legislation to hold digital platforms accountable for preventing online harms and ensuring user safety.
Social Media and Children’s Well-Being
- Potential Harms:
- Research indicates that social media usage may adversely affect children’s mental health, exposing them to cyberbullying, inappropriate content, and excessive screen time.
- Balancing Risks and Benefits:
- While social media offers educational and social benefits, a blanket ban may be an overly simplistic approach. Critics, including academics and policymakers, argue for nuanced solutions over outright restrictions.

Criticism and Concerns
- Effectiveness of the Ban:
- The Australian Greens have termed the legislation “rushed” and “ineffective,” arguing it oversimplifies complex issues without addressing underlying risks comprehensively.
- Implementation Challenges:
- Ambiguity around “reasonable steps” and potential overreach in data collection have raised concerns among privacy advocates and researchers.
Significance for Policy and Governance
- Global Implications:
- Australia’s law could set a precedent for other nations addressing the dual challenge of protecting minors online and upholding privacy.
- Way Forward:
- Policies must balance regulatory frameworks with inclusivity, leveraging technology to create a safer digital environment while avoiding excessive restrictions.
- Promoting digital literacy and fostering collaborations among governments, platforms, and civil society could enhance effectiveness.
Conclusion
The Online Safety Amendment (Social Media Minimum Age) Bill, 2024 is a commendable step towards safeguarding children from online harm. However, its success depends on the effective implementation of privacy safeguards, stakeholder consultation, and addressing practical challenges. A balanced approach, combining regulation with education and awareness, will be essential to achieve the desired outcomes while upholding the rights of all users.