The challenge of holding judges accountable
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus: GS II Polity
Context: Recent incidents of judicial misconduct in India have reignited debates on mechanisms to ensure accountability within the judiciary. These events underscore the urgent need for transparency and responsibility in judicial actions to maintain public trust and uphold democratic principles. For instance, a speech by Justice Shekhar Kumar Yadav, revealing apparent biases against the Muslim community, highlights the deficiencies in India’s mechanisms for holding higher judiciary judges accountable.
What is Judicial Accountability?
Judicial accountability refers to the principle that judges must be answerable for their decisions and actions, ensuring that they operate transparently and within the ambit of the law. It is fundamental to sustaining public trust and maintaining the judiciary’s credibility in a democratic framework.
Provisions for Judicial Accountability
Constitutional Provisions:
- Article 124(4) and 124(5): Provide for the impeachment of Supreme Court judges for proven misconduct or incapacity.
- Article 217: Governs the impeachment of High Court judges on similar grounds.
- Article 235: Empowers High Courts to supervise and control subordinate courts.
- Restatement of Judicial Values (1997): Acts as a voluntary code of conduct for members of the higher judiciary.
Legal Provisions:
- Judges (Inquiry) Act, 1968: Establishes a framework for investigating judicial misconduct through a three-member panel.
- Contempt of Courts Act, 1971: Ensures the judiciary functions independently, free from external influence.
- Judicial Standards and Accountability Bill (pending): Seeks to enhance judicial transparency and introduce stronger oversight mechanisms.
Need for Judicial Accountability
- Ensuring Public Trust:
- Sustains the credibility of the judiciary and reinforces citizens’ confidence in the justice delivery system.
- Preventing Misconduct:
- Promotes adherence to ethical standards and constitutional values.
- Enhancing Transparency:
- Allows judicial decisions to be scrutinized, fostering fairness and impartiality.
- Balancing Independence with Responsibility:
- Prevents misuse of judicial independence for personal or political interests.
- Promoting Rule of Law:
- Guarantees decisions that are unbiased, equitable, and aligned with constitutional principles.
Examples of Judicial Accountability
- Justice Soumitra Sen’s Impeachment (2011):
- Found guilty of financial misconduct during his tenure as a court-appointed receiver, demonstrating parliamentary oversight.
- Justice P.D. Dinakaran’s Resignation (2011):
- Resigned amid allegations of land grabbing and corruption, highlighting the role of public and institutional scrutiny.
- RTI and Judiciary (2020):
- The Supreme Court upheld the applicability of the Right to Information Act, ensuring transparency in judicial appointments and functioning.
Challenges to Judicial Accountability
- Impeachment Complexity:
- The impeachment process is arduous, requiring a two-thirds majority in Parliament.
- Limited Oversight Mechanisms:
- Absence of robust external monitoring frameworks to evaluate judicial behavior.
- Independence Concerns:
- Overemphasis on accountability could compromise judicial autonomy.
- Resignations Before Proceedings:
- Judges often resign to evade inquiries, stalling accountability efforts.
- Lack of Transparency:
- Closed-door deliberations reduce public confidence in judicial processes.

Way Ahead
- Legislative Reforms:
- Expedite the passage of the Judicial Standards and Accountability Bill to establish structured oversight mechanisms.
- Strengthening Internal Mechanisms:
- Create independent judicial review bodies to monitor ethical compliance and behavior.
- Codifying Ethical Guidelines:
- Update and enforce the Restatement of Judicial Values to address contemporary challenges.
- Public Scrutiny:
- Promote transparency by regularly publishing judgments, judicial activities, and decisions.
- Training and Awareness:
- Conduct regular ethical training for judges to foster a deeper commitment to constitutional principles.
Conclusion
Judicial accountability is pivotal for preserving the judiciary’s independence and integrity. Transparent mechanisms, coupled with institutional reforms, are essential to reinforce public trust and ensure that justice delivery aligns with democratic ideals. By balancing independence with responsibility, India can fortify its judiciary as the bedrock of its constitutional democracy.
All eyes on PSLV-C60 mission as ISRO looks to end 2024 on a high
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus: GS III Science and Technology
Context: The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is poised to conclude 2024 with the highly anticipated PSLV-C60/SpaDeX mission, scheduled for launch on December 30, 2024. This mission represents a significant milestone in advancing India’s space exploration capabilities.
About SpaDeX Mission
Launch Vehicle:
- Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV-C60):
- Core-alone configuration, a reliable workhorse for medium-lift satellite launches.
Aims:
- Primary Objective:
- Demonstrate rendezvous, docking, and undocking capabilities between two spacecraft.
- Secondary Objectives:
- Transfer of electric power between docked spacecraft, essential for future robotic applications.
- Composite spacecraft control and post-docking payload operations.
Features:
- Satellites:
- Two satellites, SDX01 (Chaser) and SDX02 (Target), each weighing 220 kg.
- Orbit Placement:
- 470-km circular orbit with a 55-degree inclination.
- Progressive Docking Process:
- Starts from a 20-km separation (Far Rendezvous) and advances to a 3-meter docking distance.
- Power Transfer Demonstration:
- Post-docking, electrical power will be transferred between the two spacecraft, a critical technology for long-duration missions.

Significance of the Mission
- Foundation for Future Space Initiatives:
- Lays the groundwork for India’s ambitious Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS) and prospective lunar missions.
- Support for Advanced Missions:
- Essential for enhancing capabilities required for Gaganyaan and the construction of an Indian space station.
- Satellite Maintenance and Cost Efficiency:
- Demonstrates potential for satellite repair and refueling, significantly reducing mission costs.
- Global Collaboration:
- Strengthens India’s position to participate in international space station projects, showcasing advanced technological capabilities.
Conclusion
The SpaDeX mission represents a pivotal step in India’s space exploration journey, marking progress in critical technologies such as spacecraft docking, in-orbit power transfer, and satellite maintenance. It underscores ISRO’s commitment to achieving self-reliance in space technology and elevating India’s standing in the global space community.
From Gemini to Llama: How AI Titans Reshaped the Industry
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus: GS III Science and Technology
In a remarkably short span, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has transitioned from being a technological novelty to an indispensable tool across sectors. The transformative advances in AI during 2024 highlight how this domain has emerged as a focal point of global competition and innovation. Below is an analysis of key developments, their implications, and the broader strategic landscape in the AI sector.

Major Developments in 2024
1. The Battle Between AI Giants: OpenAI and Google
2024 witnessed an intense rivalry between OpenAI and Google, each pushing the boundaries of AI capabilities.
- Google’s Resurgence:
Following a rocky launch of its Bard chatbot, Google rebounded with its Gemini series of AI models.
- Gemini 2.0: Introduced “Flash Thinking,” significantly improving the model’s reasoning capabilities.
- Trillium AI Accelerator and Willow Quantum Chips: These technological breakthroughs bolstered investor confidence, driving Alphabet’s stock to record highs.
- Integration: Gemini’s AI was infused across Google products, setting a benchmark for functionality and efficiency.
- OpenAI’s Advancements:
Building on the success of its earlier models, OpenAI launched the o3 model, which outperformed competitors in complex coding, mathematics, and reasoning tasks.
- While o3 enhanced enterprise applications like Microsoft 365 Copilot, its increased computational costs highlighted the need for balancing performance with economic feasibility.
2. Expansion Beyond Proprietary Models
Other firms such as Anthropic and Mistral AI made significant contributions by focusing on safety, open-source innovation, and practical applications:
- Anthropic:
- Introduced Claude 3.5 Sonnet, capable of autonomous computer tasks, transforming software development processes.
- Its proactive measures during the U.S. presidential election underscored the growing focus on responsible AI deployment.
- Mistral AI:
- Released open-weight models like Mistral 7B and Mixtral 8x7B, promoting accessibility and collaborative innovation.
- Enhanced its footprint by integrating with IBM Watsonx and collaborating with Qualcomm for device-based AI.
3. Meta’s Foray into Open-Source AI
Meta advanced modular AI systems through its Llama 3 models, scaling parameter counts and integrating multimodal capabilities (text and images).
- With over 650 million downloads, Meta’s models demonstrated their growing acceptance, enhancing AI-driven features in platforms like Facebook and Instagram.
Widening Accessibility: On-Device AI
AI’s evolution in 2024 also emphasized on-device deployments, enabling real-time functionality:
- Smartphones and Tablets:
- Integration of AI chipsets (e.g., Apple’s Neural Engine, Google Tensor) allowed advanced capabilities like image processing and multimodal queries.
- PCs and Gaming Consoles:
- AI accelerators like NVIDIA GeForce and Apple’s M-series chips facilitated transcription, video editing, and gaming advancements, broadening consumer and enterprise use cases.
The Talent Imperative
At the heart of AI advancements lies a dual-engine system: data training and inference. However, talent is the true engine driving innovation:
- Brain Drain at OpenAI: The departure of key personnel like co-founder Ilya Sutskever and CTO Mira Murati created challenges, as rivals like Anthropic absorbed some of this talent.
- Global Mobility of AI Experts: Studies show nearly 11 out of 100 AI specialists relocate internationally every five years. Countries and firms that attract top talent are better positioned to lead in AI innovation.
Strategic Implications
- Global Competitiveness:
- Open-source initiatives by Mistral and Meta contrast with proprietary models like OpenAI’s, fostering democratization of AI innovation.
- Investments in quantum computing and AI accelerators underscore a race to control strategic resources.
- National Policy Focus:
- To maintain leadership, nations must prioritize education, research, and talent acquisition in AI-related domains.
- Collaboration between governments and private players, as seen with Anthropic’s safety measures, is critical to ensuring ethical AI use.
- Economic and Social Transformation:
- On-device AI integration highlights AI’s role in everyday life, from smartphones to consumer electronics.
- As firms like Apple approach a $4 trillion valuation, AI is emerging as a key driver of economic growth.
Conclusion
The year 2024 marked a pivotal phase in the AI revolution, defined by fierce competition, technological breakthroughs, and growing global interdependence. For nations and companies, the ability to foster innovation, attract talent, and navigate ethical challenges will determine their position in this transformative era. AI’s integration into diverse sectors not only underscores its ubiquity but also highlights its potential to redefine the global technological order.
India Records Lowest Internet Shutdowns in Eight Years: A Critical Analysis
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus: GS II Polity and Governance
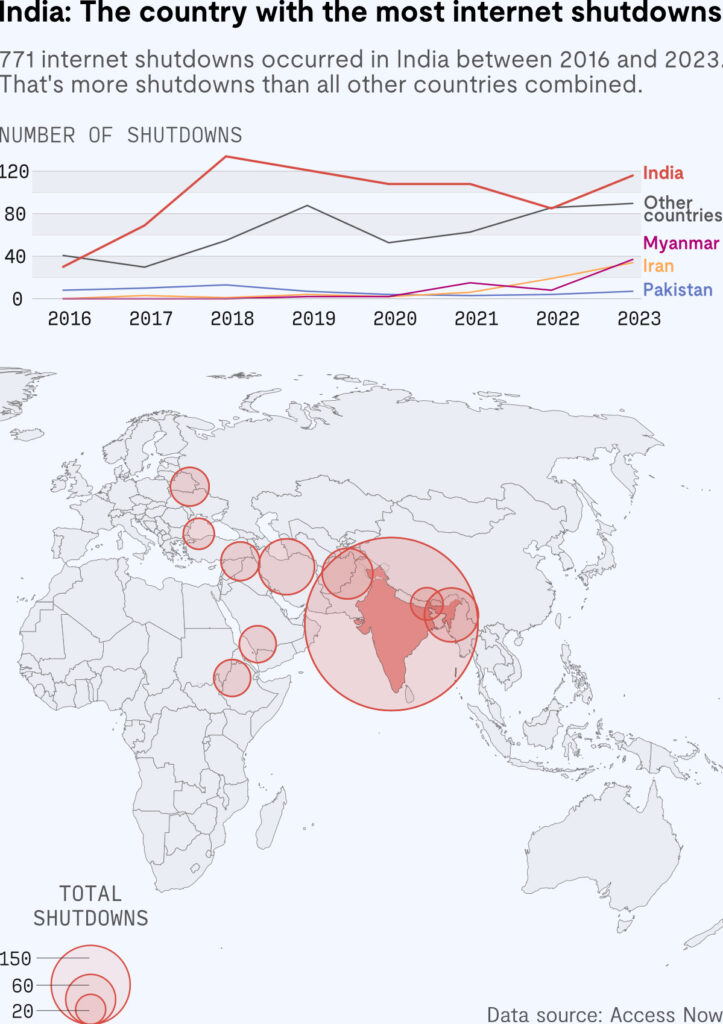
India witnessed 60 Internet shutdowns in 2024, marking the lowest number in eight years, according to the Internet Shutdowns Tracker by the Software Freedom Law Centre (SFLC). This represents a significant decline from the 96 shutdowns in 2023 and a peak of 132 in 2020, following the revocation of Article 370 in Jammu and Kashmir. Despite this reduction, India remains the world’s most frequent user of Internet shutdowns as a measure to address unrest.
Regional Trends and Reasons for Shutdowns
- Major Areas of Impact:
Jammu and Kashmir and Manipur, historically responsible for a large share of shutdowns, saw fewer instances in 2024. However, some shutdowns were still reported in these regions due to law and order concerns. For example:
- Manipur: Internet access was suspended in nine districts owing to ongoing unrest.
- Haryana: Ambala experienced a shutdown during planned farmer agitations.
- Policy Dynamics:
Shutdowns are typically imposed for a fixed number of days but are often extended. Each extension is treated as a fresh shutdown by the SFLC, contributing to higher counts in prior years.
Legal and Policy Concerns
- Non-Compliance with Supreme Court Judgments:
Despite the landmark Bhasin vs. Union of India (2020) judgment mandating the publication of shutdown orders, States frequently fail to comply. Courts have repeatedly reprimanded authorities for this non-compliance. - Absence of Centralised Data:
The Union government has stated in Parliament that it does not maintain centralised records of Internet shutdowns. The lack of a unified database complicates the evaluation of the practice’s efficacy and impact. - No Studies on Efficacy or Economic Impact:
Successive governments have admitted in Parliament that no study has been conducted to assess:
- The economic cost of Internet shutdowns on sectors like education, tourism, and business.
- The efficacy of shutdowns as a tool to address public emergencies or unrest.
Arguments For and Against Shutdowns
- Government’s Position:
The Union government defends Internet shutdowns as necessary to balance public safety with the risk of misuse by anti-social elements. Union Minister of State for Communications Pemmasani Chandra Sekhar reiterated this stance in a December 2024 Rajya Sabha response. - Criticism by Digital Rights Activists:
Activists argue that shutdowns are both unnecessary and ineffective. They highlight the disruption to essential services, education, and business operations, alongside violations of digital rights. Advocacy group Access Now criticized the continued misuse of shutdowns, stating that officials fail to adhere to legal requirements for publishing orders.
Implications and Way Forward
- Economic and Social Costs:
- Internet shutdowns disrupt education, healthcare, and businesses, especially in rural areas that rely on digital platforms.
- A study on the economic and social costs of shutdowns is imperative to evaluate their utility against their adverse effects.
- Policy Reform:
- The absence of centralised data and studies underscores the need for greater accountability and transparency in the imposition of Internet shutdowns.
- A comprehensive framework to regulate shutdowns, with a focus on minimizing disruptions, is essential.
- Judicial Oversight:
- Strengthened judicial scrutiny and mechanisms for grievance redressal can ensure that shutdowns are imposed only as a last resort.
- Balancing Rights and Security:
- Policymakers must strike a balance between safeguarding national security and preserving citizens’ digital rights, as Internet access is increasingly viewed as a fundamental necessity.
Conclusion
The reduction in Internet shutdowns in 2024 is a positive development, but India’s continued status as the world leader in imposing such measures raises questions about their necessity, efficacy, and impact. Greater transparency, accountability, and adherence to judicial guidelines are critical for ensuring that Internet shutdowns are used judiciously and do not undermine the digital aspirations of a rapidly modernizing nation.